eISSN : 3022-7011
ISSUER : KIPS
ISSUER : KIPS
After the Korea Information Processing Society (KIPS) Transactions journal was founded in 1994, it was reorganized into the KIPS Transactions: Computer and Communication Systems(2287-5891/2734-049X ) and the KIPS Transactions: Software and Data Engi neering(2287-5905/2734-0503) in 2012. Through the KIPS official meeting on January 8th, 2024, the new KIPS Transaction journal was founded by integrating two KIPS Journals, KIPS Transactions: Computer and Communication Systems and KIPS Transactions: Software and Data Engineering. The new journal aims to realize social value and contribute to the development of South Korea’s science and technology with support from the lottery fund of the Ministry of Strategy and Finance and the science/technology promotion fund of the Ministry of Science and ICT. It is indexed in the Korea Science Academic Database, Korea Citation Index (KCI), and EBSCO.
HighlightsMore
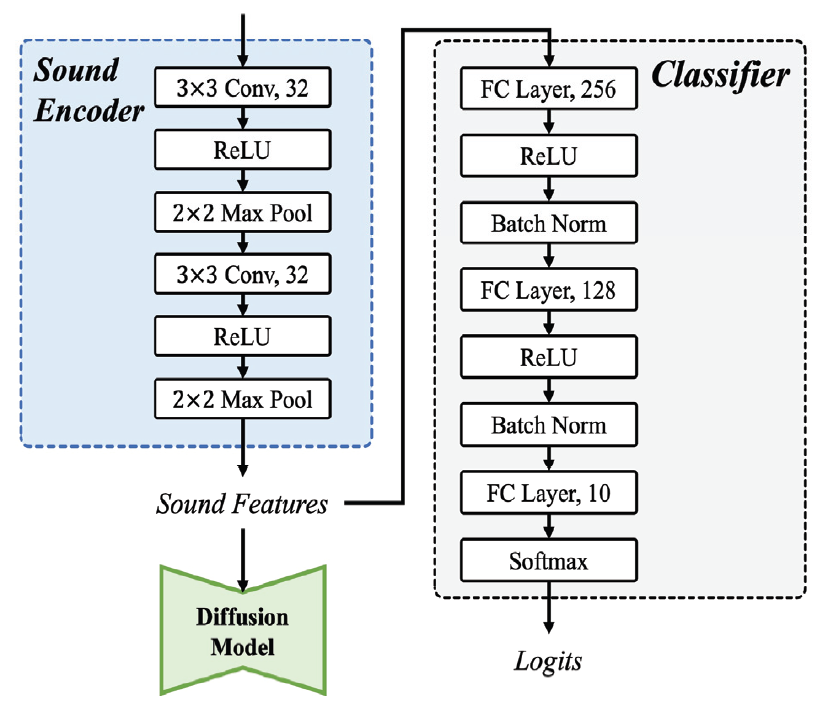
Diffusion-based Audio-to-Visual Generation for High-Quality Bird ImagesAdel Toleubekova Joo Yong Shim XinYu Piao Jong-Kook Kim |
|
| Accurately identifying bird species from their vocalizations and generating corresponding bird images is still a challenging task due to limited training data and environmental noise in audio data. To address this limitation, this paper introduces a... | |
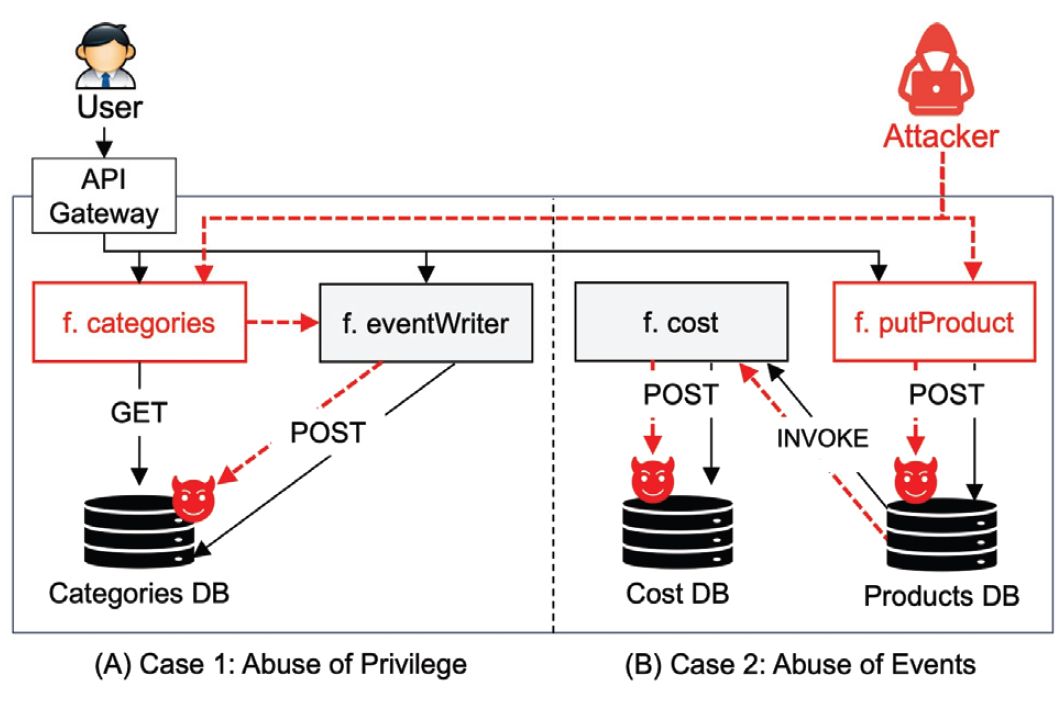
Bambda: A Framework for Preventing Function Invocation Condition-Based Attacks in Serverless EnvironmentsShin Chang Hee Lee Seung Soo |
|
| Serverless computing is rapidly emerging as a new paradigm in cloud computing, offering automatic scalability, cost efficiency, and ease of operation. However, its two core characteristics—IAM-based privilege management and event-driven execution—ca... | |
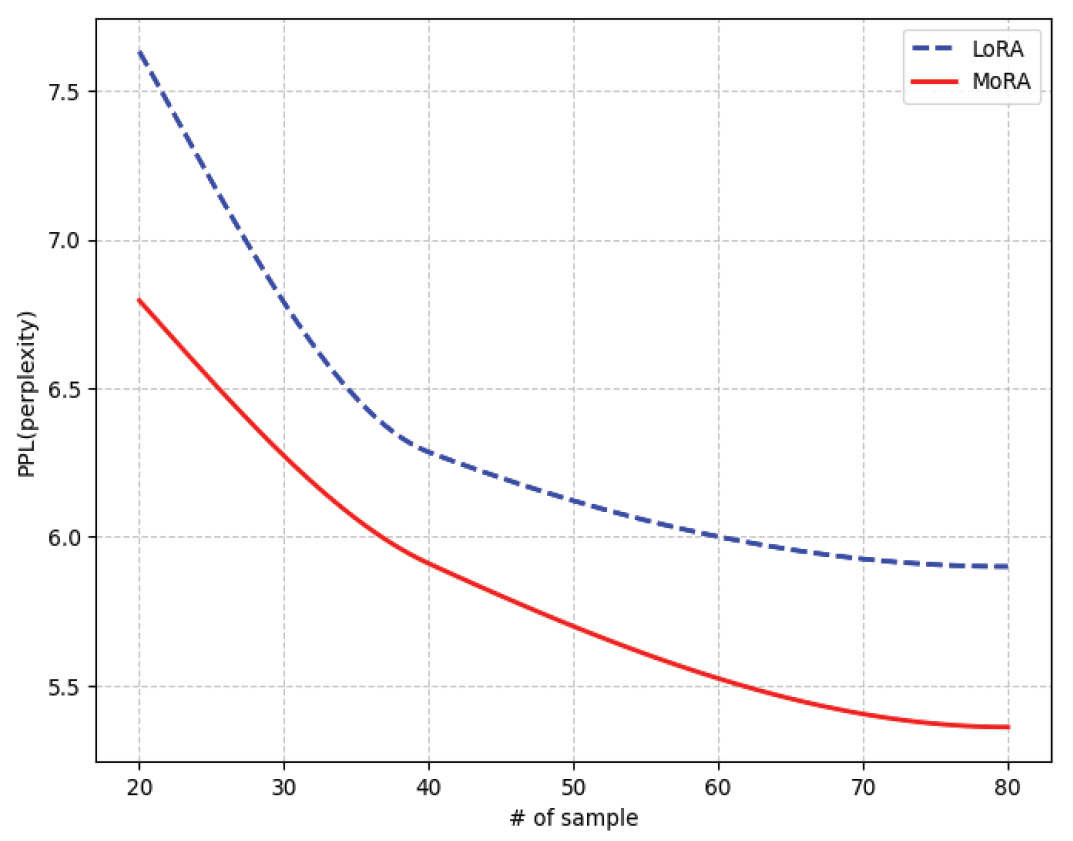
PEFT Methods for Domain AdaptationLee You Jin Yoon Kyung Koo Chung Woo Dam |
|
| This study analyzed that the biggest obstacle in deploying Large Language Models (LLMs) in industrial settings is incorporating domain specificity into the models. To mitigate this issue, the study compared model performance when domain knowledge wa... | |
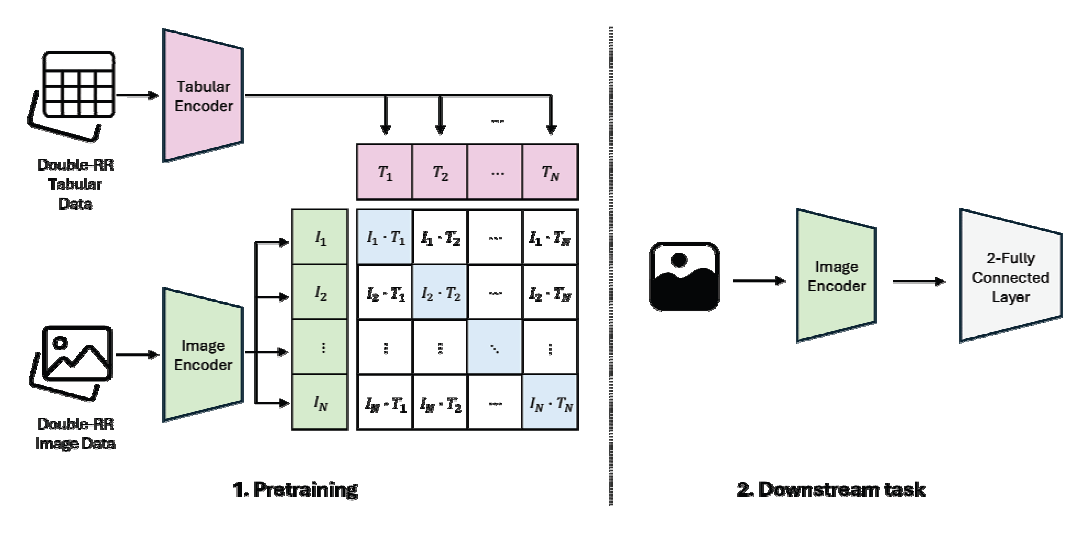
Label Differential Privacy Study for Privacy Protection in Multimodal Contrastive Learning ModelYoungseo Kim Minseo Yu Younghan Lee Ho Bae |
|
| Recent advancements in multimodal deep learning have garnered significant attention from both academia and industry due to their exceptional accuracy and ability to learn rich knowledge representations. In particular, contrastive learning based appr... | |
Latest Publication (Vol. 14, No. 12, Dec. 2025)
Design and Implementation of an Integrated Framework for Lifecycle Management of Cloud Resources
Junwoo Park Jaehyeon Kim Hyun Ahn Sung Hyun Lee Yeseung Lee Choong-Hee Cho
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.987
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.987
Cloud Automation Resource Provisioning Lifecycle Management Version Control System
This paper presents a lightweight framework that automates the full lifecycle of cloud resources—from creation to extension, expiration,
and deletion—via a command-based interface integrated with a configuration management system. Unlike prior approaches limited to
initial resource deployment automation, the proposed architecture supports intuitive lifecycle control with minimal manual intervention.
The system is composed of a user portal, an automation bot server, and CSP plugins, which interact through RESTful APIs to ensure
modularity and extensibility. Experimental evaluation shows that the framework achieves a 71% reduction in provisioning time compared
to manual console operations and demonstrates high stability and reproducibility.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 987-996,
Dec.
2025
Cloud Automation Resource Provisioning Lifecycle Management Version Control System
Impact of Utterance Length and Augmentation on Spoofed Sppech Detection
Gyuhan Hwang MinJe Seok Wooseong Kim
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.997
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.997
ASVspoof 5 SSD Augmentation
ASVspoof 5 is the fifth edition of the ASVspoof challenge, one of the largest global audio security challenges, aiming to promote the
development of Countermeasure(CM) models by distinguishing between genuine and spoofed speech. In this study, we investigate the
impact of data augmentation and utterance length on spoofed speech detection(SSD) using pretrained speech models. XLSR, WavLM, and
HuBERT are used as feature extractors, and a dual-branch network proposed in previous studies is also used. To evaluate robustness,
five data augmentation techniques and three different utterance lengths are tested. Most augmentation methods degrade performance,
while Low Frequency Mask augmentation achieves an EER of 6.36% and a min-DCF of 0.1676. Experiments on utterance length show
that a 8-second duration yields the best performance. The results demonstrate that both augmentation strategies and utterance duration
have a significant impact on SSD performance. These findings provide insights into the factors affecting robustness in ASVspoof 5-based
spoofed speech detection.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 997-1003,
Dec.
2025
ASVspoof 5 SSD Augmentation
MLSQ: A Multimodal-based System for Learning Material Summarization and Question Generation
Geonwoo Yu Sangyoon Lee Jinyoung Ahn Minha Woo Sugyeong Kim Jungoo Lee Hyeonwoo Choi Yaeran Kim Woonghee Lee
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1004
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1004
Multimodal Automatic Question Generation Learning Material Summarization Large Language Model Optical Character Recognition
While the proliferation of digital learning environments has increased the use of diverse multimedia materials, this often leads to passive
learning. Existing text-based automatic question generation technologies are insufficient to overcome this limitation. Therefore, this study
proposes an AI-based system (MLSQ) that integrates and analyzes video lectures and written materials. This system precisely fuses text
data extracted via OCR and STT, along with handwriting information detected from the lecture video as a key emphasis point, based
on temporal information and inputs it into a Large Language Model (LLM) to summarize learning content and automatically generate
both short-answer and multiple-choice questions. Performance evaluation results showed that the proposed multimodal fusion method
demonstrated improved performance over single-modal approaches, with a maximum increase of 3.4%p in BLEU score and 3.1%p in
ROUGE-L score. Furthermore, in a 5-point Mean Opinion Score (MOS) user evaluation, the system demonstrated its educational practicality
and effectiveness by achieving high scores above 4.0 in all categories, with ‘Speech Conversion Reliability’ and ‘Learning Suitability of
Question Generation’ receiving an average of 4.33.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1004-1015,
Dec.
2025
Multimodal Automatic Question Generation Learning Material Summarization Large Language Model Optical Character Recognition
User Interface for Real-Time Multi-Criteria Decision Making Support
Jang Woo Young Kim Eun Jee
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1016
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1016
Multi-criteria decision making Decision Matrix User Interface Cognitive Load
This study aims to propose a user interface method to support flexible and rapid decision-making in dynamic battlefield environments
where Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) is required. To this end, the study identifies limitations of the traditional decision matrix
commonly used in MCDM and suggests improvements to the user interface that take into account the characteristics and limitations of
human cognitive ability. These improvements include presenting information in linguistic formats and setting minimum threshold values
for each criterion. The proposed approach is illustrated through a hypothetical battlefield scenario to demonstrate its effectiveness. The
user interface considerations presented in this study are expected to enhance real-time decision-making by enabling more adaptable
and swift responses in complex operational environments. The significance of this research lies in applying human-centered interface
elements to the decision matrix, thereby offering potential improvements in real-time multi-criteria decision making support.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1016-1021,
Dec.
2025
Multi-criteria decision making Decision Matrix User Interface Cognitive Load
DF-LogGraph: An Explainable GraphRAG-Based Framework for Digital Forensic Log Analysis
Jeong In Lee Moohong Min
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1022
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1022
Digital Forensics RAG LLM log analysis XAI
In digital forensics, logs serve as critical evidence for reconstructing the timing of incidents and the activities of actors. Previous studies
have mainly focused on anomaly detection or single-event explanations, without extending toward actor-centric timeline reconstruction
or legally admissible explainable analyses that preserve temporal continuity and session context. To address these limitations, we propose
DF-LogGraph, a framework that normalizes logs into Actor, Action, Target, Time, and Session slots, and transforms them into a log-graph
to enable structured narrative modeling. In the query stage, DF-LogGraph applies GraphRAG with temporal and session constraints to
selectively retrieve relevant sessions and subgraphs. In the generation stage, it enforces line ID/session citations, Minimal Sufficient Evidence
Sets (MSES), and counterfactual validation to mitigate hallucinations and logical contradictions. Experiments on the LogHub–HDFS and
UNSW-NB15 datasets show that DF-LogGraph consistently outperforms BM25 (keyword-based) and a Hybrid baseline (BM25 ∪ TF-IDF)
in terms of Evidence F1@10 and Session Accuracy@10, while maintaining practical mean latency for interactive analysis. Moreover, it
improves evidence coverage, reduces hallucination rates, and ensures causal consistency through counterfactual validation. These results
demonstrate that DF-LogGraph goes beyond improving retrieval accuracy: it enhances actor-centric timeline reconstruction, reinforces
session and temporal coherence, and ensures explainability with legal reliability positioning itself as a next-generation framework for
digital forensic log analysis.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1022-1029,
Dec.
2025
Digital Forensics RAG LLM log analysis XAI
A Study on Authentication Methods for Shared-access Devices Based on the Matter Standard
Ran Kyung Kim Min Ah You Min Seok Kim Jae Beom Lee Dong-Young Yoo
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1030
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1030
Matter Standard Token-Based Authentication Device Authentication Time-Limited Access Control
With the convenience and security provided by the Matter standard, many companies have recently developed appliances based
on this standard. The Matter standard employs security mechanisms such as network and user authentication, OTA authentication,
and session-based control, which allow only authenticated users to access devices. However, in environments such as hotels or shared
offices, requiring all users to undergo prior authentication is cumbersome and procedurally complex. In this paper, we propose a
temporary token authentication method that enables smart home devices to be controlled without prior authentication by issuing
short-term tokens. The proposed method grants a check-in token via QR code at check-in, immediately revokes the token at check-out,
and, if necessary, issues a refresh token to restrict IoT device control privileges within a limited time period. An application was
developed to register the Tapo L535E bulb via QR code and control its power and color, demonstrating that Matter-based devices
can be remotely controlled.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1030-1036,
Dec.
2025
Matter Standard Token-Based Authentication Device Authentication Time-Limited Access Control
A Method for Classifying Users based on Their Capacitive Touchscreen Usage Characteristics
Hohyeon Lim Seyoung Lee
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1037
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1037
Multi-Factor Authentication Security IoT/Embeded System Usable Security biometrics
Modern computing environments are evolving from personal devices such as traditional PCs and smartphones to devices used by a
broad, unspecified user base such as Internet-of-Things and embedded devices. These devices employ touchscreens and touchpads to
interact with users and simultaneously display information. Because they are used by many different people and often have limited
resources, such devices typically rely only on simple authentication methods like passwords or PINs. However, such simple methods not
only fail to meet the security requirements of modern Internet environments but also serve as an attack surface. This study demonstrates
that users can be classified by the physical characteristics of touchscreens and by users’ behavioral traits, and proposes a secondary
authentication method that performs dynamic user authentication based on that classification.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1037-1043,
Dec.
2025
Multi-Factor Authentication Security IoT/Embeded System Usable Security biometrics
A Study on the Blocking of Malicious Behavior of Generative AI Input Prompts Using Small Language Model Module
Mun Jong In Ryu Dong Hoon Dong-Young Yoo
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1044
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1044
Prompt Injection Pre-Inference Small Language Model (SLM) Guardrails
Large language models (LLMs) are useful for search, coding, and agentic workflows, but because input prompts directly control their
behavior, they are vulnerable to prompt injection (direct and indirect), jailbreaks, format/Unicode evasion, resource exhaustion, and misuse
of tools/plugins. We propose a pre-inference prompt model that filters and blocks risks before any model call by combining a lightweight
global classifier with threat-specific small language model (SLM) modules, routing by calibrated confidence and policy mapping, and
removing format evasions through preprocessing such as Unicode normalization/decoding and suffix sanitization. Our evaluation on public
benchmarks and real-world scenarios reports block-failure rate, over-blocking rate, latency and cost, calibration error, and domain-related
metrics. We also present integration with multi-agent defenses and post-hoc moderation, along with a deployment guide grounded in
least-privilege, provenance verification, and isolation principles.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1044-1050,
Dec.
2025
Prompt Injection Pre-Inference Small Language Model (SLM) Guardrails
Towards Automated Vulnerability Analysis in ARM-based Virtualization
Dongha Lee Gyujeong Jin Geonha Lee Daehyeon Ko Jaewon Yang Hyungyu Oh
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1051
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1051
ARM Virtualization Nested Virtualization vulnerability Analysis Fuzzing
This study systematically analyzes the attack surface of ARM-based virtualization in comparison with x86 and proposes a methodology
for identifying ARM-specific vulnerabilities. The methodology comprises three stages—extraction of address-translation, coverage-guided
fuzzing, and multi-layered detection. In particular, provides reproducible instrumentation procedures and a cross-validation framework
for low-level mechanisms such as NV and the TLB, enabling practitioners to rapidly detect and confirm issues in ARM environments.
Applied to KVM/arm64, the methodology revealed and reproduced two concrete vulnerabilities: an ASID matching error and a TLB
invalidation-range calculation error. We addressed both with small patches and validated the fixes using the proposed observation
procedure, demonstrating a practical approach to vulnerability analysis in ARM virtualization.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1051-1057,
Dec.
2025
ARM Virtualization Nested Virtualization vulnerability Analysis Fuzzing
A Text Mining Analysis of Research on WTO Disputes
Jang Seo Jun Kim Kyung Yeul Kim Ji Hie
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1058
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1058
Text Mining WTO Disputes TF-IDF Word2vec keyword network Research Trends
As the scope of trade disputes expands into various areas such as digital and security issues, the need for a more systematic analysis
of research topics and trends has increased. However, there is a lack of quantitative analyses on trade dispute-related research topics
and trends in domestic studies. This study aims to analyze the major research themes and trends in WTO (World Trade Organization)
disputes using text mining techniques. Specifically, TF-IDF, Word2Vec, and keyword network analysis are employed. The results indicate
that domestic research on WTO disputes has expanded from traditional trade conflict topics to include normative conflicts related to
digital and security issues. Moreover, the research tends to focus on country-specific characteristics and event-driven analyses. The findings
of this study offer analytical insights into the research trends and key themes in the field of trade disputes, thereby contributing to future
research.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1058-1064,
Dec.
2025
Text Mining WTO Disputes TF-IDF Word2vec keyword network Research Trends
Design and Usability Evaluation of User-Friendly Security Tools
Ju Hye Lee Yoo Jin Lee Mi So Yang Sungwook Kim
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1065
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1065
Manuscript IoT Usable Security User-Friendly Design Non-Expert Users user study
With the rapid proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, convenience in daily life has increased, but so have various security
threats. However, most existing security tools are designed for experts, making them difficult for general users to understand and utilize.
This study aims to design and develop a user-friendly IoT security interface, “Jikeobom,” that enables non-expert users to easily engage
in protective actions, and to empirically verify its effectiveness. Screenshots of existing tools (e.g., Windows Defender, Nmap) and the
proposed interface were presented to participants, who evaluated perceived usability (PU), actionability (AC), trust (TR), intention to use
(IU), and cognitive load (CL). A total of 34 non-expert participants took part in the study. The results showed that the proposed interface
achieved significantly higher scores than conventional tools in PU, AC, and IU (p < .001, d > 1.2). TR also showed a moderate level of
improvement (d = 0.56), while CL showed no significant difference. Qualitative feedback indicated that intuitive explanations and guidance
messages reduced hesitation and encouraged immediate protective behaviors. These results empirically demonstrate that usability-centered
design of security interfaces can promote adoption and protective behavior among non-expert users, providing practical implications
for the design of user-friendly security interfaces in IoT environments.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1065-1072,
Dec.
2025
Manuscript IoT Usable Security User-Friendly Design Non-Expert Users user study
Real-time 3D Projection Map Interaction based on Dynamic Object Tracking
Kim Hang Kee Kim Ki Hong Baek Nak Hoon
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1073
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1073
Spatial Augmented Reality Dynamic Projection Mapping Human-Computer Interaction Projector-Camera System
In this paper, we propose a projection mapping-based interactive system that projects images onto the surface of moving objects
in real time and controls 3D content. Projection mapping in dynamic scenes suffers from system latency due to the recognition of moving
surfaces and subsequent projection. The proposed technique compensates for distortion through depth camera-projector calibration and
addresses the latency issue through a Kalman filter and hysteresis-based double-edge technique. The proposed technique compensates
for distortion through depth camera-projector compensation and tracks object movement, shifting images from the background to the
foreground, and altering animation and content flow based on object movement. Projection latency was measured in tens of milliseconds,
and intuitive interaction and high immersion were demonstrated through the "Magic Cube" demonstration content.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1073-1083,
Dec.
2025
Spatial Augmented Reality Dynamic Projection Mapping Human-Computer Interaction Projector-Camera System
Efficient Graph Convolutional Networks Update for Expanded Single Large Graph
Song Jee Yeon Lee Ki Yong
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1084
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1084
Graph Neural Networks Expanded Single Large Graph Fine-Tuning
Graph Neural Networks(GNNs) are typically trained on static graphs whose structures remain unchanged. However in real-world
scenarios, graphs expand as new nodes and edges are added, requiring the model to be retrained on the entire graph to reflect these
updates. The fine-tuning method, often used to mitigate the inefficiency of full retraining, also faces limitations when applied to GNNs;
due to the message passing mechanism, improvements in computational efficiency are restricted, and the performance on original nodes
often declines. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an efficient Graph Convolutional Networks(GCN) update for expanded
single large graphs. The proposed method maximizes computational efficiency by decomposing the message passing operation into two
components: pre-computed information from the pre-training and newly required computations. Furthermore it alleviates performance
degradation on original nodes, a problem by setting all nodes in the expanded graph as the training target. Experimental results on
real-world datasets demonstrate that our proposed method significantly reduces training time compared to full retraining and fine-tuning,
while maintaining a performance level comparable to that of full retraining.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1084-1090,
Dec.
2025
Graph Neural Networks Expanded Single Large Graph Fine-Tuning
Build Automation Framework for RTEMS Custom Schedulers
Taehan Kim Seongmin Park Geumsook Heo Joonhyouk Jang
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1091
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1091
RTEMS Custom Scheduler Build Automation Waf Build System
RTEMS (Real-Time Executive for Multiprocessor Systems) provides a flexible kernel structure that supports user-defined scheduler
integration. Since version 6.1, the transition to the Waf build system has made this integration process more complex, requiring manual
edits to multiple configuration files and causing frequent build errors. To overcome these challenges, we propose the RTEMS Custom
Scheduler Framework, which automates code template generation, configuration file registration, and kernel build execution. This reduces
the integration process from 4–5 manual steps to a single GUI-based step, enabling developers to focus solely on scheduling logic.
Experimental results with priority, simple, and EDF schedulers achieved a 100% success rate, demonstrating improved efficiency, stability,
and usability in real-time kernel extension development.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1091-1096,
Dec.
2025
RTEMS Custom Scheduler Build Automation Waf Build System
Deep Learning-Based Non-Linear Prediction of Remaining Useful Life of Aircraft Engines
Min-Jung Kim Kang-Won Lee
 10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1097
10.3745/TKIPS.2025.14.12.1097
Remaining useful life prediction Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) Deep Learning Aircraft Turbofan Engines C-MAPSS Dataset
The prediction of the remaining useful life (RUL) of aircraft turbofan engines is a critical task in prognostics and health management
(PHM), as it enables the early detection of component degradation, the optimization of maintenance schedules, and the prevention of
safety incidents. Recent deep learning–based RUL prediction studies have made significant progress. However, most efforts have focused
on improving model architectures, while relatively little attention has been paid to the design of RUL labeling functions. This study proposes
a novel approach that preserves the existing pre-training structure used in recent research while replacing the target RUL labeling function
with a non-linear concave function that more accurately reflects actual degradation patterns. Using the NASA C-MAPSS (Commercial
Modular Aero-Propulsion System Simulation) dataset, we evaluate a CAE (convolutional autoencoder)–RNN-based prediction model under
various parameter settings and demonstrate that the proposed non-linear labeling model improves prediction accuracy in terms of RMSE
(root mean squared error) and simultaneously enhances the NASA S-score safety metric compared to the conventional piecewise-linear
model.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 1097-1104,
Dec.
2025
Remaining useful life prediction Prognostics and Health Management (PHM) Deep Learning Aircraft Turbofan Engines C-MAPSS Dataset


 Korean
Korean