eISSN : 3022-7011
ISSUER : KIPS
ISSUER : KIPS
After the Korea Information Processing Society (KIPS) Transactions journal was founded in 1994, it was reorganized into the KIPS Transactions: Computer and Communication Systems(2287-5891/2734-049X ) and the KIPS Transactions: Software and Data Engi neering(2287-5905/2734-0503) in 2012. Through the KIPS official meeting on January 8th, 2024, the new KIPS Transaction journal was founded by integrating two KIPS Journals, KIPS Transactions: Computer and Communication Systems and KIPS Transactions: Software and Data Engineering. The new journal aims to realize social value and contribute to the development of South Korea’s science and technology with support from the lottery fund of the Ministry of Strategy and Finance and the science/technology promotion fund of the Ministry of Science and ICT. It is indexed in the Korea Science Academic Database, Korea Citation Index (KCI), and EBSCO.
HighlightsMore
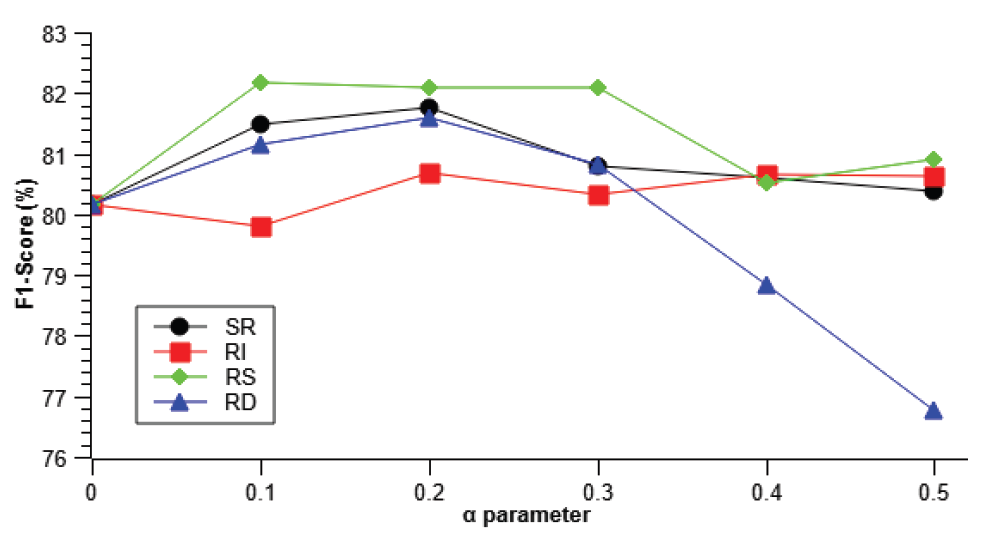
A Study on Improving Performance of Software Requirements Classification Models by Handling Imbalanced DataJong-Woo Choi Young-Jun Lee Chae-Gyun Lim Ho-Jin Choi |
|
| Software requirements written in natural language may have different meanings from the stakeholders’ viewpoint. When designing an architecture based on quality attributes, it is necessary to accurately classify quality attribute requirements because... | |
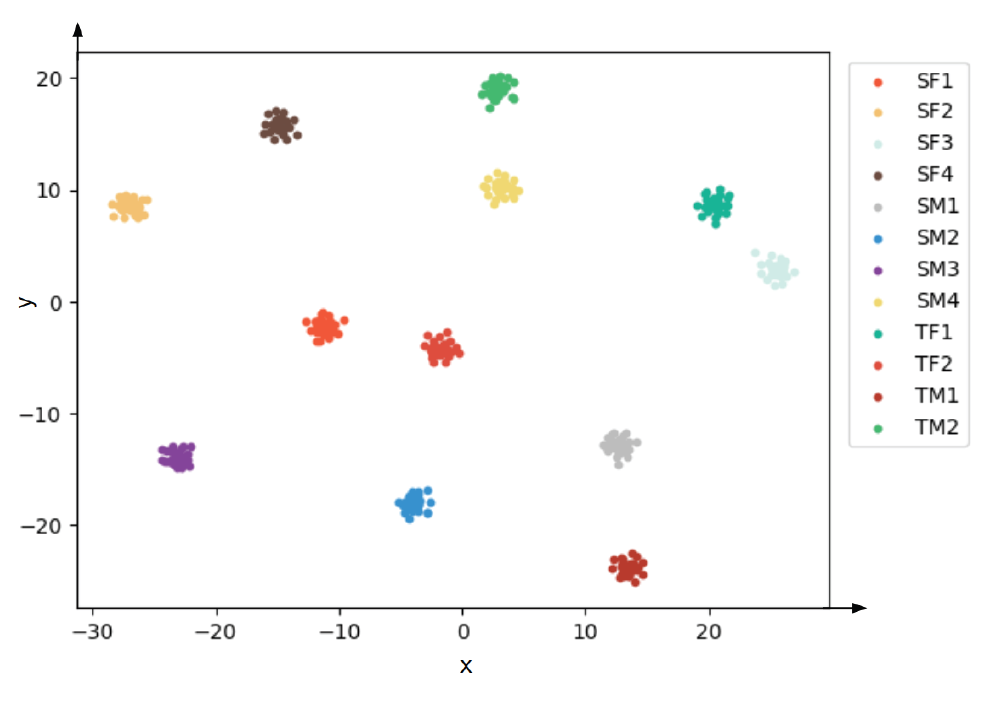
Extending StarGAN-VC to Unseen Speakers Using RawNet3 Speaker RepresentationBogyung Park Somin Park Hyunki Hong |
|
| Voice conversion, a technology that allows an individual’s speech data to be regenerated with the acoustic properties(tone, cadence, gender) of another, has countless applications in education, communication, and entertainment. This paper proposes a... | |
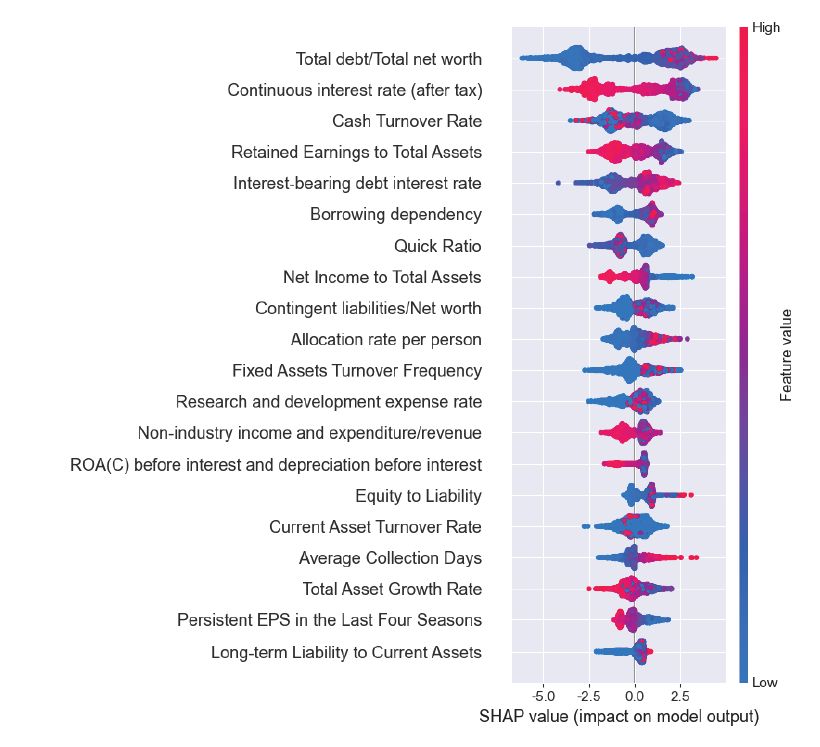
A Study on Classification Models for Predicting Bankruptcy Based on XAIJihong Kim Nammee Moon |
|
| Efficient prediction of corporate bankruptcy is an important part of making appropriate lending decisions for financial institutions and reducing loan default rates. In many studies, classification models using artificial intelligence technology hav... | |
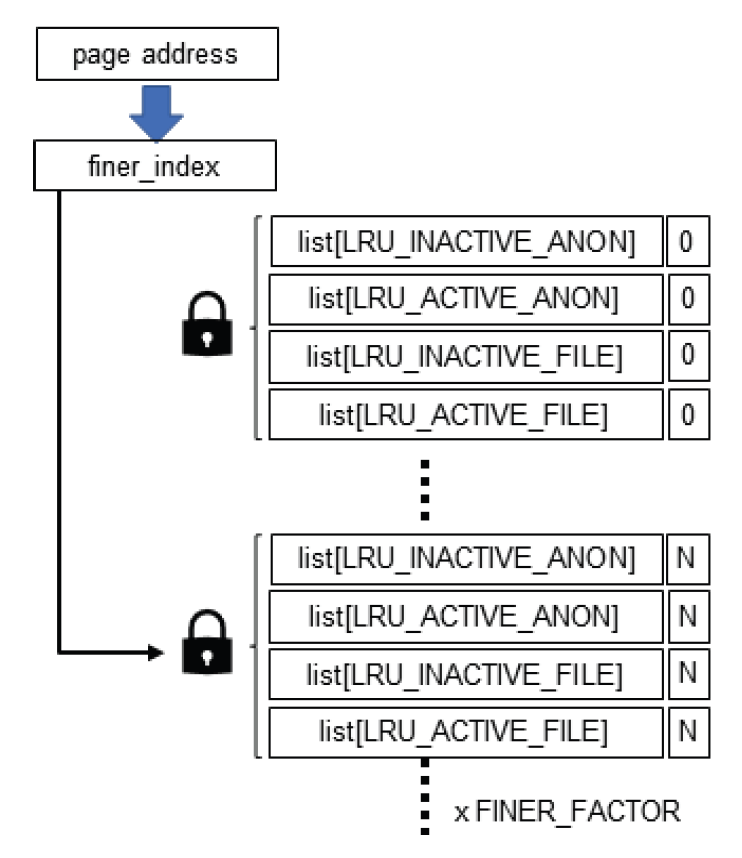
Detecting Common Weakness Enumeration(CWE) Based on the Transfer Learning of CodeBERT ModelChansol Park So Young Moon R. Young Chul Kim |
|
| Recently the incorporation of artificial intelligence approaches in the field of software engineering has been one of the big topics. In the world, there are actively studying in two directions: 1) software engineering for artificial intelligence an... | |
Latest Publication (Vol. 13, No. 4, Apr. 2024)
Attention Based Collaborative Source-Side DDoS Attack Detection
Hwisoo Kim Songheon Jeong Kyungbaek Kim
 https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.157
https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.157
DDoS Collaborative Source-Side Attack Detection Attention
The evolution of the Distributed Denial of Service Attack(DDoS Attack) method has increased the difficulty in the detection process.
One of the solutions to overcome the problems caused by the limitations of the existing victim-side detection method was the source-side
detection technique. However, there was a problem of performance degradation due to network traffic irregularities. In order to solve
this problem, research has been conducted to detect attacks using a collaborative network between several nodes based on artificial
intelligence. Existing methods have shown limitations, especially in nonlinear traffic environments with high Burstness and jitter. To
overcome this problem, this paper presents a collaborative source-side DDoS attack detection technique introduced with an attention
mechanism. The proposed method aggregates detection results from multiple sources and assigns weights to each region, and through
this, it is possible to effectively detect overall attacks and attacks in specific few areas. In particular, it shows a high detection rate
with a low false positive of about 6% and a high detection rate of up to 4.3% in a nonlinear traffic dataset, and it can also confirm
improvement in attack detection problems in a small number of regions compared to methods that showed limitations in the existing
nonlinear traffic environment.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 157-165,
Apr.
2024
DDoS Collaborative Source-Side Attack Detection Attention
Lip and Voice Synchronization Using Visual Attention
Dongryun Yoon Hyeonjoong Cho
 https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.166
https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.166
입술-음성 동기화 시각적 어텐션 트랜스포머
본 연구에서는 얼굴 동영상에서 입술의 움직임과 음성 간의 동기화 탐지 방법을 제안한다. 기존의 연구에서는 얼굴 탐지 기술로 얼굴 영역의
바운딩 박스를 도출하고, 박스의 하단 절반 영역을 시각 인코더의 입력으로 사용하여 입술-음성 동기화 탐지에 필요한 시각적인 특징을 추출하였다.
본 연구에서는 입술-음성 동기화 탐지 모델이 음성 정보의 발화 영역인 입술에 더 집중할 수 있도록 사전 학습된 시각적 Attention 기반의 인코더
도입을 제안한다. 이를 위해 음성 정보 없이 시각적 정보만으로 발화하는 말을 예측하는 독순술(Lip-Reading)에서 사용된 Visual Transformer
Pooling(VTP) 모듈을 인코더로 채택했다. 그리고, 제안 방법이 학습 파라미터 수가 적음에도 불구하고 LRS2 데이터 세트에서 다섯 프레임 기준으로
94.5% 정확도를 보임으로써 최근 모델인 VocaList를 능가하는 것을 실험적으로 증명하였다. 또, 제안 방법은 학습에 사용되지 않은 Acappella
데이터셋에서도 VocaList 모델보다 8% 가량의 성능 향상이 있음을 확인하였다.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 166-173,
Apr.
2024
입술-음성 동기화 시각적 어텐션 트랜스포머
Efficient Emotion Classification Method Based on Multimodal Approach Using Limited Speech and Text Data
Mirr Shin Youhyun Shin
 https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.174
https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.174
Artificial intelligence Natural Language Processing speech recognition Multimodal Emotion classification
In this paper, we explore an emotion classification method through multimodal learning utilizing wav2vec 2.0 and KcELECTRA models.
It is known that multimodal learning, which leverages both speech and text data, can significantly enhance emotion classification
performance compared to methods that solely rely on speech data. Our study conducts a comparative analysis of BERT and its derivative
models, known for their superior performance in the field of natural language processing, to select the optimal model for effective feature
extraction from text data for use as the text processing model. The results confirm that the KcELECTRA model exhibits outstanding
performance in emotion classification tasks. Furthermore, experiments using datasets made available by AI-Hub demonstrate that the
inclusion of text data enables achieving superior performance with less data than when using speech data alone. The experiments show
that the use of the KcELECTRA model achieved the highest accuracy of 96.57%. This indicates that multimodal learning can offer meaningful
performance improvements in complex natural language processing tasks such as emotion classification.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 174-180,
Apr.
2024
Artificial intelligence Natural Language Processing speech recognition Multimodal Emotion classification
Token-Based Classification and Dataset Construction for Detecting Modified Profanity
Sungmin Ko Youhyun Shin
 https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.181
https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.181
Artificial intelligence Natural Language Processing named entity recognition Profanity ChatGPT
Traditional profanity detection methods have limitations in identifying intentionally altered profanities. This paper introduces a new
method based on Named Entity Recognition, a subfield of Natural Language Processing. We developed a profanity detection technique
using sequence labeling, for which we constructed a dataset by labeling some profanities in Korean malicious comments and conducted
experiments. Additionally, to enhance the model's performance, we augmented the dataset by labeling parts of a Korean hate speech
dataset using one of the large language models, ChatGPT, and conducted training. During this process, we confirmed that filtering the
dataset created by the large language model by humans alone could improve performance. This suggests that human oversight is still
necessary in the dataset augmentation process.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 181-188,
Apr.
2024
Artificial intelligence Natural Language Processing named entity recognition Profanity ChatGPT
Region of Interest Extraction and Bilinear Interpolation Application for Preprocessing of Lipreading Systems
Jae Hyeok Han Yong Ki Kim Mi Hye Kim
 https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.189
https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.189
Artificial neural network region of interest interpolation Object Detection Lipreading
Lipreading is one of the important parts of speech recognition, and several studies have been conducted to improve the performance
of lipreading in lipreading systems for speech recognition. Recent studies have used method to modify the model architecture of lipreading
system to improve recognition performance. Unlike previous research that improve recognition performance by modifying model
architecture, we aim to improve recognition performance without any change in model architecture. In order to improve the recognition
performance without modifying the model architecture, we refer to the cues used in human lipreading and set other regions such as
chin and cheeks as regions of interest along with the lip region, which is the existing region of interest of lipreading systems, and compare
the recognition rate of each region of interest to propose the highest performing region of interest In addition, assuming that the difference
in normalization results caused by the difference in interpolation method during the process of normalizing the size of the region of
interest affects the recognition performance, we interpolate the same region of interest using nearest neighbor interpolation, bilinear
interpolation, and bicubic interpolation, and compare the recognition rate of each interpolation method to propose the best performing
interpolation method. Each region of interest was detected by training an object detection neural network, and dynamic time warping
templates were generated by normalizing each region of interest, extracting and combining features, and mapping the dimensionality
reduction of the combined features into a low-dimensional space. The recognition rate was evaluated by comparing the distance between
the generated dynamic time warping templates and the data mapped to the low-dimensional space. In the comparison of regions of
interest, the result of the region of interest containing only the lip region showed an average recognition rate of 97.36%, which is 3.44%
higher than the average recognition rate of 93.92% in the previous study, and in the comparison of interpolation methods, the bilinear
interpolation method performed 97.36%, which is 14.65% higher than the nearest neighbor interpolation method and 5.55% higher than
the bicubic interpolation method. The code used in this study can be found a https://github.com/haraisi2/Lipreading-Systems.
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 189-198,
Apr.
2024
Artificial neural network region of interest interpolation Object Detection Lipreading
Analyzing the Impact of Multivariate Inputs on Deep Learning-Based Reservoir Level Prediction and Approaches for Mid to Long-Term Forecasting
Hyeseung Park Jongwook Yoon Hojun Lee Hyunho Yang
 https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.199
https://doi.org/10.3745/TKIPS.2024.13.4.199
Reservoir Water Level Prediction Fully Connected Neural Network Multivariate Inputs
Local reservoirs are crucial sources for agricultural water supply, necessitating stable water level management to prepare for extreme
climate conditions such as droughts. Water level prediction is significantly influenced by local climate characteristics, such as localized
rainfall, as well as seasonal factors including cropping times, making it essential to understand the correlation between input and output
data as much as selecting an appropriate prediction model. In this study, extensive multivariate data from over 400 reservoirs in
Jeollabuk-do from 1991 to 2022 was utilized to train and validate a water level prediction model that comprehensively reflects the complex
hydrological and climatological environmental factors of each reservoir, and to analyze the impact of each input feature on the prediction
performance of water levels. Instead of focusing on improvements in water level performance through neural network structures, the
study adopts a basic Feedforward Neural Network composed of fully connected layers, batch normalization, dropout, and activation
functions, focusing on the correlation between multivariate input data and prediction performance. Additionally, most existing studies
only present short-term prediction performance on a daily basis, which is not suitable for practical environments that require medium
to long-term predictions, such as 10 days or a month. Therefore, this study measured the water level prediction performance up to one
month ahead through a recursive method that uses daily prediction values as the next input. The experiment identified performance
changes according to the prediction period and analyzed the impact of each input feature on the overall performance based on an Ablation
study
The Transactions of the Korea Information Processing Society,
Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 199-207,
Apr.
2024
Reservoir Water Level Prediction Fully Connected Neural Network Multivariate Inputs


 Korean
Korean